T-Tests
Compare means with t-tests
What You'll Learn
- One-sample t-test
- Two-sample t-test
- Paired t-test
- When to use each
What is a T-Test?
Purpose: Test if means are significantly different
Three types:
- One-sample: Compare sample to known value
- Two-sample: Compare two groups
- Paired: Compare before/after
One-Sample T-Test
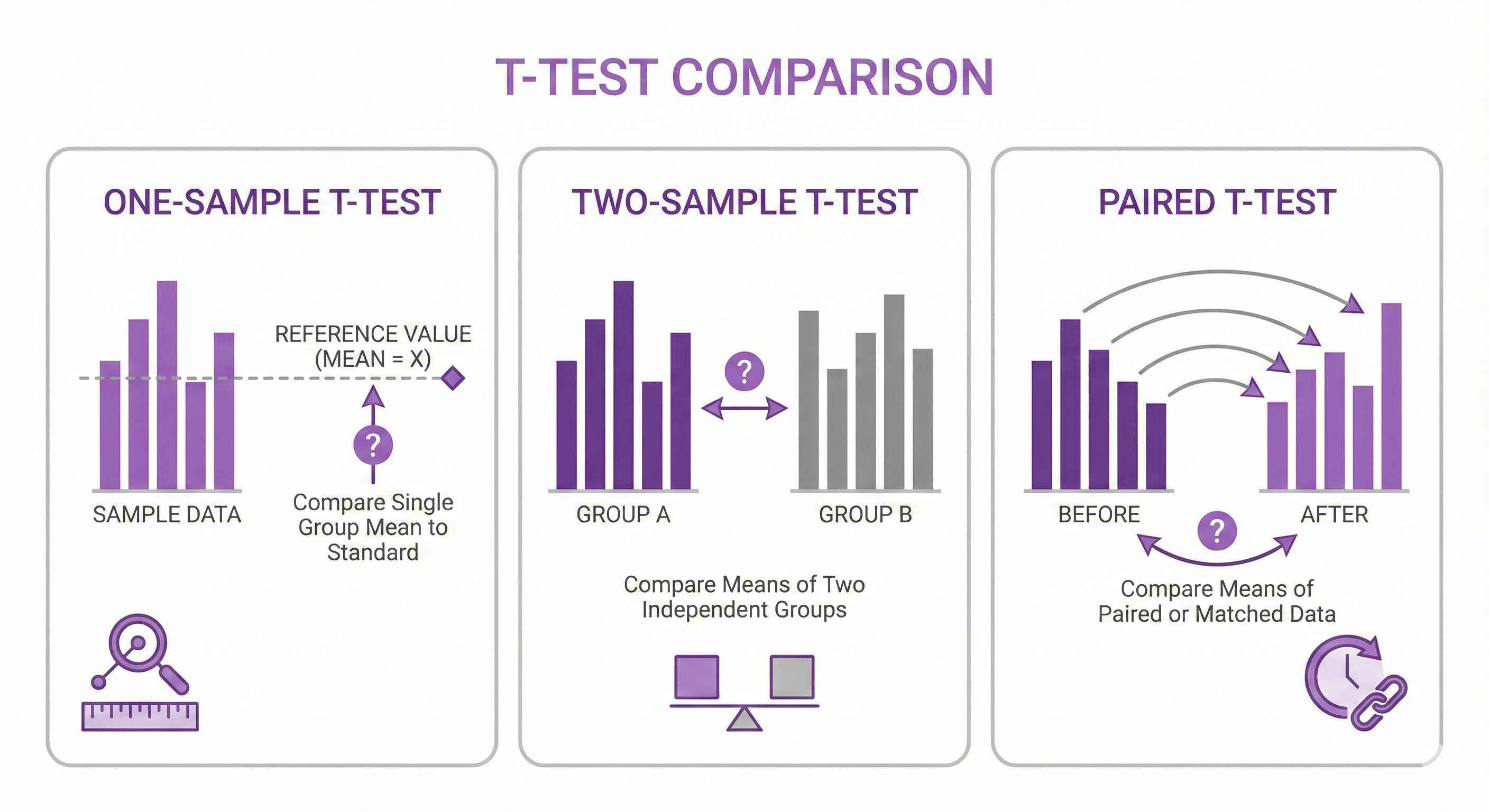
Question: Is sample mean different from known value?
Example: Average height is 170cm. Is your sample different?
Hypotheses:
- H0: μ = 170 (null)
- H1: μ ≠ 170 (alternative)
Excel: =T.TEST(range, 170, 2, 1) Python: scipy.stats.ttest_1samp(data, 170)
Two-Sample T-Test
Question: Are two group means different?
Example: Do men and women have different average salaries?
Types:
- Independent: Different groups
- Equal variance assumed
- Unequal variance (Welch's)
Excel: =T.TEST(group1, group2, 2, 2) Python: scipy.stats.ttest_ind(group1, group2)
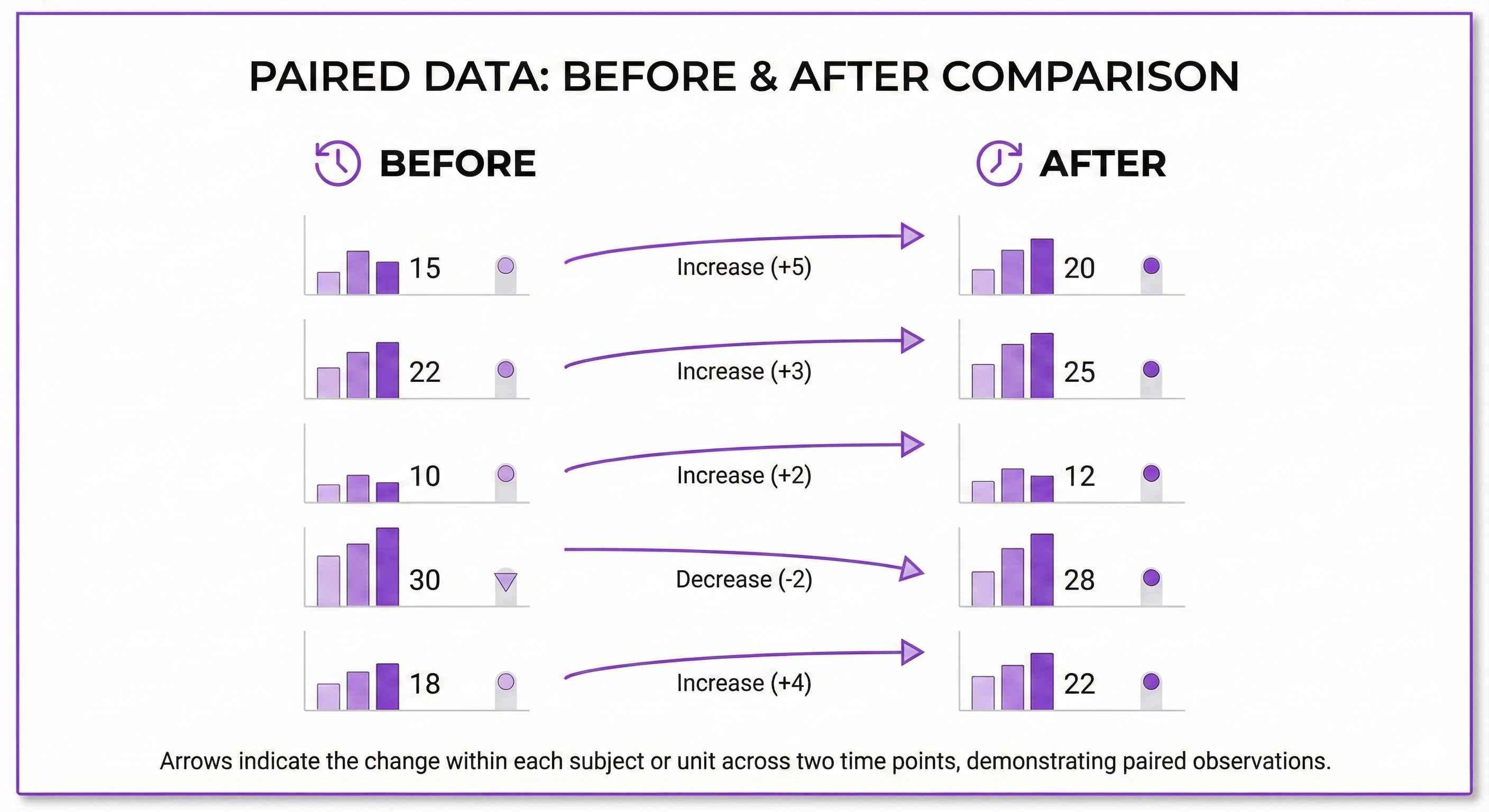
Paired T-Test
Question: Is there difference before vs after?
Example: Weight before vs after diet (same people)
Key: Same subjects measured twice!
Excel: =T.TEST(before, after, 2, 1) Python: scipy.stats.ttest_rel(before, after)
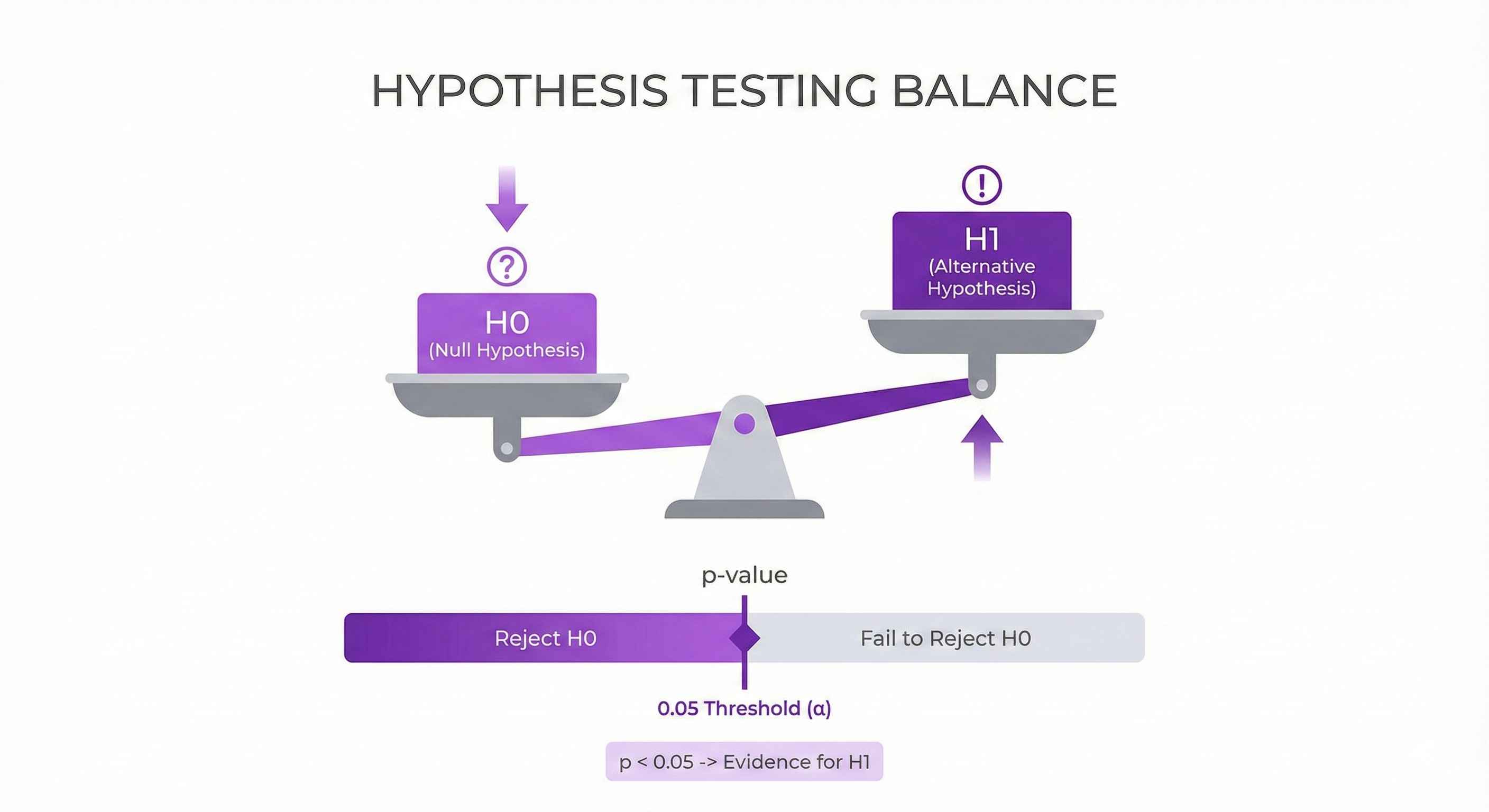
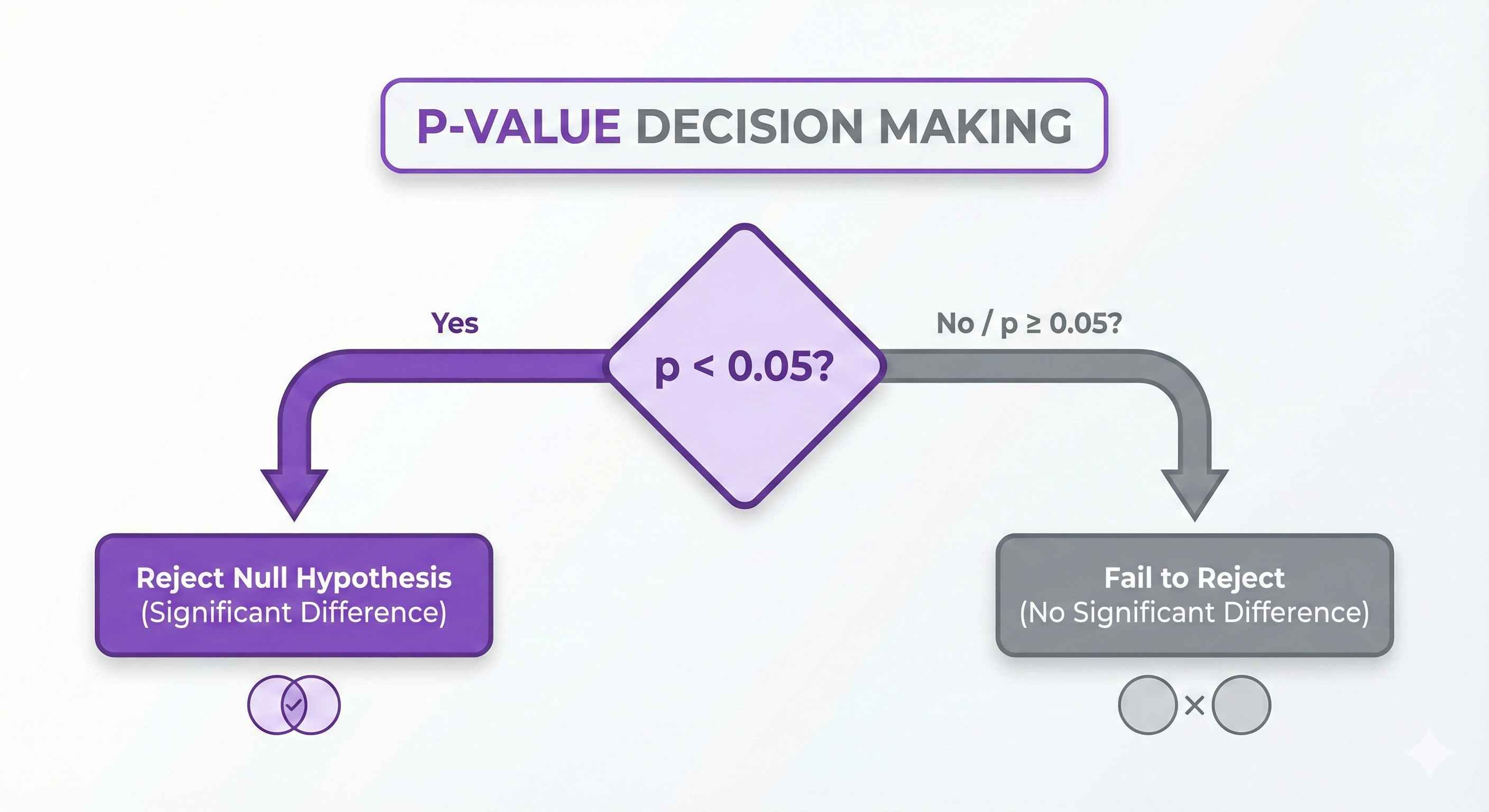
P-Value
What it means: Probability of seeing this result if null hypothesis is true
Decision rule:
- p < 0.05: Reject null (significant!)
- p ≥ 0.05: Fail to reject null
Example: p = 0.03 → Reject null (groups ARE different)
Assumptions
T-tests assume:
- Normal distribution (or large sample)
- Independent observations
- For two-sample: Equal variances (or use Welch's)
Check before testing!
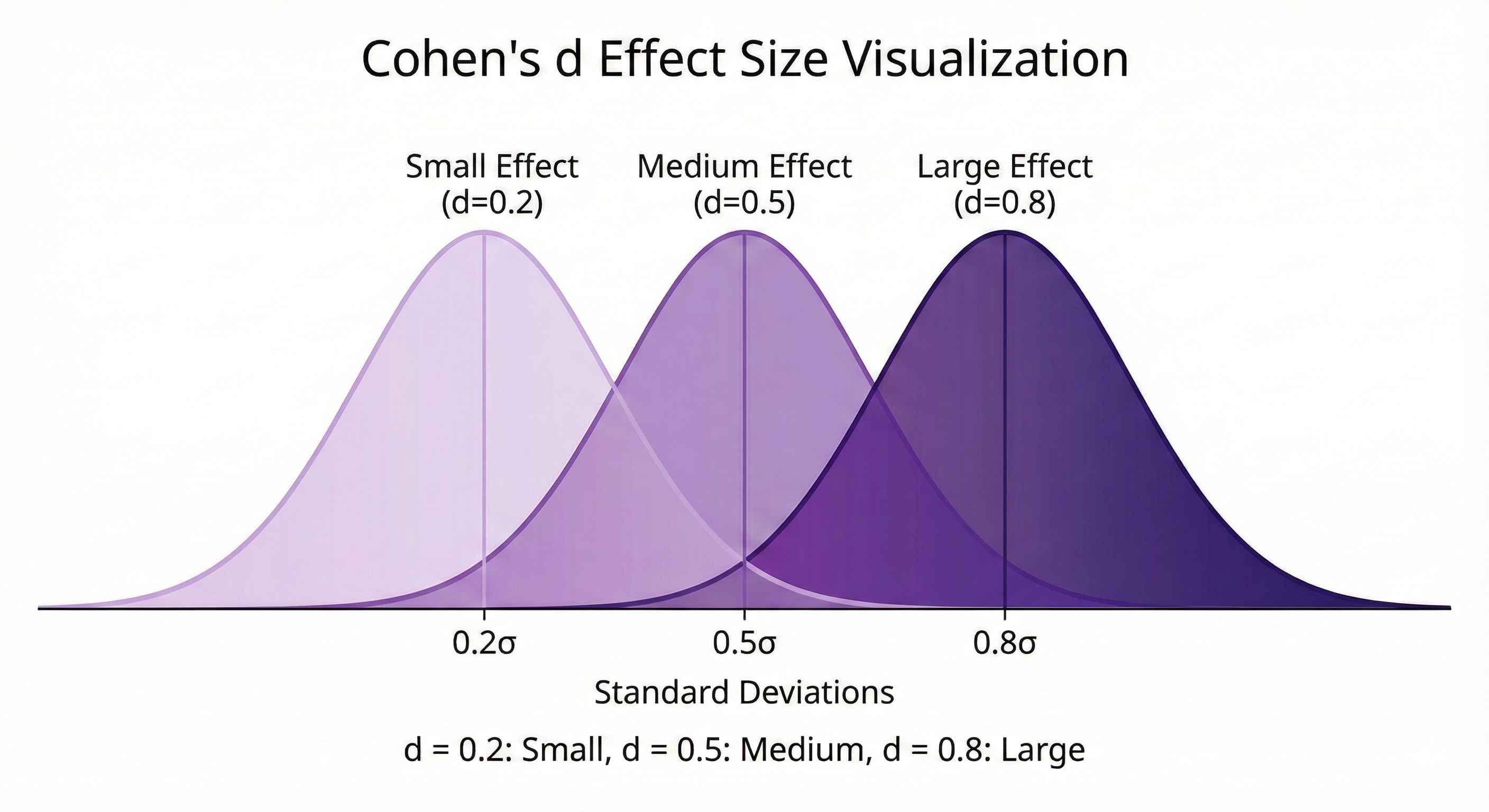
Effect Size
Statistical significance ≠ Practical significance
Cohen's d: d = (Mean1 - Mean2) / Pooled SD
Interpretation:
- d = 0.2: Small
- d = 0.5: Medium
- d = 0.8: Large
Practice Exercise
Group A: 80, 85, 90, 95, 100 Group B: 70, 75, 80, 85, 90
Conduct two-sample t-test. Are they different?
Next Steps
Learn about Chi-Square Tests!
Tip: Always check assumptions before running t-test!